
Avocado (Persea americana)
Local names in Kenya (Parachichi in swahili)
Overview
Avocado is a perennial fruit tree crop native to the Americas but grows well in Kenya. It is very nutritious with a high protein and oil content and is becoming increasingly important as an export crop. Nutritionally the avocado oil is cholesterol free, of the monounsaturated type believed to protect against heart disease and certain kinds of cancers. The fruit is nearly sodium free, is rich in potassium dietary fibre and vitamin B6, C, D and E. It is eaten as fresh fruit, in salads, soups, ice cream, also used to make avocado oil, perfume and avocado paste. Areas It is an important commercial fruit in Kenya both for local and export markets
Altitude range
Avocado will thrive well at 200 to 1000 masl
Soil type and conditions
Deep soil, with good water holding capacity and free draining.It requires a pH: 5.5 – 6.5
Avocado nutrient requirements include; N, P, K, Mg, Ca, Na, B, S, Zn, Mn, Fe, Cu, Al, Mo
Temperature range
The temperatures should be 16 – 24 oC. Above 33oc fruits suffer heat damage, below 4oc impaired growth of tree
Rainfall
Rainfall of 600 mm is essential during production period
Steps during land preparation
- Clear the field of trees, bushes and weeds
- Prepare only planting holes
- Prepare, in advance, planting holes 60cm x 60cm x 60cm
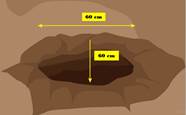
- Separate topsoil and sub soil
- Spacing may range from 6m x 6m, 6m x 7m or 8m x 10m between trees depending on growth characteristic of the individual variety and the type of soil
Nursery site selection
Ensure; nearness to quality water source, good drainage, security from animals, thieves etc, and accessibility to the road and availability of wind breaks e.g. Casuarina, Grevillea etc
Nursery establishment
Prepare a seedbed of width 1 m and a desirable length by removing farm soil from the seedbed to a depth of 30 cm and refill the 30 cm depression with sand
Seed preparation
Collect seed only from healthy and vigorous mother trees and from fruits which are mature and healthy rather than from off the ground
Large sized seeds generally produces vigorous seedlings
Cultivars used as rootstocks are Puebla or Local varieties, Fuerte is not resistant to Phytophthora
Extracted seeds should be treated in hot water not exceeding 50 ºC for 30 minutes
Coat or dipped in a broad spectrum fungicide e.g. Metalaxyl to prevent infection with Phytophthora cinnamoni
Sowing seeds
Plant seeds with the flat basal end pointing downwards either in nursery beds or directly into eco-bags, about 20 cm in diameter and 30 cm deep
Transplanting
About 20 days after germination, plant should be 20 cm high and having developed two pairs of leaves
Transplant open seeded seedlings in nursery beds by uprooting and planting into containers
Potting media should be medium texture, sterilized if possible and with good drainage properties
Grafting
The rootstocks are ready for grafting 6 months after transplanting into biodegradable containers 6 X 9 inches
The rootstocks are grafted using scions of desired variety
4 to 6 months later, the seedlings are ready for transplanting into the field and should be well healed and free from pests and diseased
Hass and Fuerte are the most preferred by the consumers
Orchard establishment
Water the hole just before planting to ensure contact of the roots with moist soil
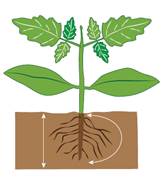
Remove the eco-bag and hold the soil media around the roots
Maintain the position of the level of soil as it was in the eco-bag while planting and firm the soil around the planted seedling
Water well and mulch after transplanting
Water young plants frequently for proper establishment
Do hand watering 2 to 3 times per week for planted seedlings for four weeks
Irrigate grown up trees at 10-15 days interval from fruit set to maturity
Irrigation can also be applied to stimulate flowering after a distinct dry spell
Explore drip irrigation bottle in dry regions
Irrigation is not recommended for 2 – 3 months prior to flowering as it is likely to promote vegetative growth at the expense of flowering
There should be a marked season with dry weather for flowering and fruiting
Keep the orchard weed free in the early stages of growth
In mature trees, weed 2 m strip along the rows and cut grass in the rest of the field
Mix one debe (20 kg) of well decomposed manure and 125 g of DAP with topsoil and return the soil to the hole dug earlier to refill the hole
In the early years, avocado require high levels of nitrogen but after they begin to bear, the fertilizer should be higher in phosphate and potash
Apply 1 debe 20 -30kg of well-decomposed manure annually: The quantity of manure applied increases with age of the crop; 4 debes each year at an optimum production from 7th year
Spread fertilizer or manure around the drip line of tree canopy and mix with the soil. Applied in a ring at the beginning of rains
Under dry conditions, the hole should be bigger about 90 x 90 cm and 100 cm deep
For irrigated orchard apply the same quantity of manure any time of the year but this should be followed by increased application of irrigation
For Top dressing fertilizer use 120-130 g of CAN or 50-60 g of Urea per stoo
Pruning
Pruning is done at an early stages before the plant starts to flower
Pruning may also be done after harvesting the internal dormant stage of crop development

Pruning
Common pests of avocado include;
- Red spider mites
- Avocado thrips
- White flies
- Fruit fly
- Fruit bug

Major diseases include;
- Scab
- Cercospora fruit spot
- Anthracnose

- Scales

Scab - infonet-biovision.org
Cercospora fruit spot - infonet-biovision.org

Anthracnose - infonet-biovision.org

Avocado root rot
Caused by poorly drained soils and flood prone areas
Anthracnose
Mostly attacks mature seeds forming dry ,dark spots
Control
Prune dead branches and twigs
Spray with appropriate fungicides e.g. dithiocarbamates, at interval of 7-10 days depending on weather conditions
Spray copper-based fungicides e.g. Nordox or copper oxychloride. Repeat every 14 days
Curative chemical e.g Topsin
Roots of other tree bushes harbour fungal pathogens that affect avocado roots
Powdery Mildew
The fungus attacks all forms of young tissues of most importance to growers are fruit panicles and young fruits. In severe attacks, the entire blossom panicle may be infected, and the fruits fail to set
Control
Foliar sprays with protective and curative fungicides as appropriate
Spraying should start at 20 % blossom then continue at about 3 weeks interva

Maturity indices include; Change in colour from green to black or purple in dark varieties
Fruit stems turn yellow and the fruit skin may sometimes turn lessy shinny
The end of the green varieties may develop rust-like spot
Fruits float on the surface when immersed into water
Harvesting
Avocado starts bearing within 3 years after transplanting. Peak harvest occurs between March – September in Kenya
Avocado is picked and stored at room temperature for 7- 10 days. If they soften without shrivelling, then the fruits is ready for harvesting
Fruit should be pulled from the stalk but cut off leaving a 3 cm stalk
The yield increases as the tree continues to grow.
250-300 kgs per tree per year (8-10 tonnes/acre)
Cartons should be well ventilated and should have a handle for handling
Fruit should not rub against each other during transportation
Pack the fruits in single layer in fibre board cartons, to void rubbing against each other that can shorten the shelf life of the fruits
Transport or store mango at 11oC for green fruit and 8oC for riper ones
Most varieties can store at temperatures between 10oC and 13oC with relative humidity of 85 to 90% for a storage period of between two to four months
Store the produce in a cool dry place. This will minimize internal chemical reaction that may accelerate early ripen before they reach the market
Pre-harvest practices influence the post-harvest procedures e.g. size, colour
Store the field boxes in the shade in order to minimize sunburn, loss of moisture and dust
accumulation Value addition techniques include; sorting, Cleaning, pre-cooling and grading Sorting: Remove all the field debris including
misshaped, diseased and bruised fruit
Cleaning: Use cold, clean water to remove any dirt found on the fruits
Pre-cooling: Fruits must be cooled as quickly as possible Fuerte and Hass must be
cooled to 5oC – 7oC within five hours of harvesting
Grading: Fruits are graded according to size and stage of ripening
Ensure fruits for export market are graded by the set size grades/code


Processing
Generally, Avocado is served raw (ripe), though it can be processed into juices, shakes, ice creams, dips, pastes and purees

