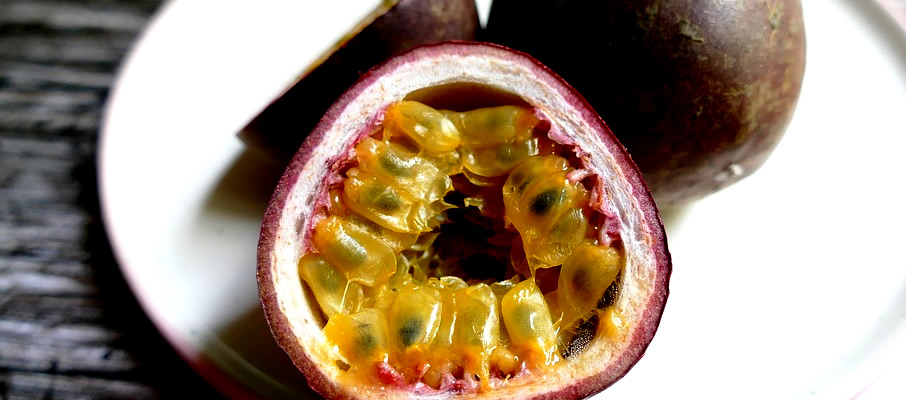

Passion fruits (Passiflora edulis)
Local names in Kenya (Matunda)
Overview
Passion fruit is a perennial climbing plant, which was introduced into Kenya in the 1920’s. It is a popular fruit for both domestic and export markets. There are two distinct forms. Forma edulis, the purple passion fruit, which does well in cool environments at higher altitudes and forma flavicarpa, the yellow passion fruit, which is known to do well in the tropical lowlands
Altitude range
Altitude requirement ranges between 0-2000 masl depending on variety e.g. Esther Variety and Purple passion require high altitude areas or cool climate at 1200-2000 masl. Sweet yellow does well in low to mid altitudes 0-1500masl
Soil type and conditions
Passion grows in a wide range of soils but performs best in light to heavy, well-drained and well-aerated sandy loams of medium texture soil. A pH of between 5.5- 7.0 is optimal. Liming is necessary if the soil is too acidic. Passion fruit requires nutrients such as; N, P, K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Fe, e Mn, Zn, S, and B
Temperature range
The temperatures should be 16-30oC, Does well in well-illuminated field e.g. adequate sunlight for flowering and fruiting
Rainfall
The rainfall should be 900-2000 mm p.a.
Steps during land preparation
- Plough deep and harrow the land 2-3 months and ensure the hard pans are removed before planting
- Prepare planting holes 45 x 45 x 45 cm
- Fill the holes with topsoil mixed with up to 10kg of compost or manure
- Add manure and fertilizers to the soil in the right amounts to provide the required plant nutrients for vigorous crop growth
Raising rootstocks for grafting
Raising rootstocks for grafting
Yellow passion recommended for grafting while purple passion fruit scions used for grafting
Seedlings as rootstocks take 2-3 months in nursery, cleft graft after 3-4 weeks when 45 cm
If cuttings are used, set them in coarse sand and later transplant into bags or a nursery bed
Grafting recommended to purple passion fruits as sweet yellow varieties already have desired rootstock characteristics
Undertake grafting, potting, adequate watering and hardening off. Grafting perpetuates hybrids for tolerance and good yields
Raising seedlings
Use seeds stored for less than 3 months
Treat seeds with hot water at 500C for 15-30 minutes. Germination takes 2-3 weeks
Raise seedlings in bags, 15cm wide and 25cm deep
Sow three seeds per bag at a depth of cm and thin after two months to leave only one
Planting can be done in pure stand or in a mixed cropping system
Transplant at 3 weeks after grafting at the start of the rainy season
Firm down the soil around the plants to establish good root and soil contact
Keep the grafted spot out of contact with soil during to avoid fungal infection
Water transplanted seedlings to ensure quick rooting and establishment of the plant
Spacing of 2 by 3m is recommended for hand cultivation and 3 by 3m for mechanized cultivation
Commercial plantations should adopt a row spacing of 1.2-1.8 m and a within-row spacing of 3m. This gives around 1900- 2700 plants per ha
Passion is heavy feeder hence appropriate fertilizer should be added during the growing season
Variety include;
Sweet yellow passion (KPF4, KPF11, KPF12), Purple passion fruit, Yellow passion, Banana passion, Giant passion, Esther variety.
Seeds


Transplanting


Plant certified seeds treated with hot water to break seed dormancy
The seedlings raised in a nursery bed grow slowly hence they are transplanted 3-4 months at a height of 15-25 cm.
Irrigation is required during dry spells but sparingly
Over irrigation may predispose the crop to root rots and other soil borne diseases
Passion fruit is sensitive to water logging.
Weed control should be done regularly.
Ensure application of 1-2 debes of manure per year per plant before rains
Foliar and trace elements should be applied at every 3 months based on the recommendations of soil testing and analysis.
Passion fruit should not be grown for more than 5 years on the same plot
Pruning and training
Trellising should be done at 2.7m high wooden posts of 15cm diameter for plants to climb and well-made metal wire used over the top of the posts
Copper wire is expensive and too soft while wooden top posts can be used however they are less durable
Train 2 healthy shoots above the graft union with sisal strings
Prune to remove old unproductive shoots and dead wood
Pruning enhances aeration and light penetration for flowers and fruits production
Pruning equipment should be sterilized to prevent contamination
All pruned plant parts should be applied copper-based fungicide to avoid fungal infection.
Pests include;
Nematodes, Leaf miner, Mealybugs, Aphids, Coreid bugs, Broad mite or yellow tea mite Caterpillars and Thrips
Nematodes


Leaf miner

Mealybugs


Aphids

Thrips


Pest control strategies
Timely weeding and pruning
Apply chill extract to repel pest
Natural enemies for aphids and mealybugs
Nematicide for nematodes
Insecticides for insects
Miticides where mite infestation is heavy
Intercropping with pest repellent crops e.g. garlic and onion.
Major diseases include;
Fusarium wilt, Brown spot, Woodiness, Septoria spot, Phytophthora, Blight, root rot
Fusarium wilt
Caused by many forms of the soil-inhabiting fungus Fusarium oxysporum

Control
Use clean seeds and remove infected plant tissues from the area and plant resistant varieties
Deep ploughing beyond 45 cm
Brown spot
Caused by Altenaria passiflora (fungal) enhanced by lack of aeration

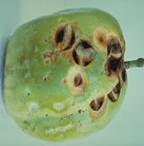
Control
Thinning vines to promote air flow
Septoria spot disease of passion fruit
Caused by fungi Alternaria spp. Prolonged rains and mild temperature favours the disease development

Control
Pruning and spraying with approved fungicides
Phytophthora blight
Caused by Phytophthora nicotianae

Control
Use of pathogen free seedlings, prune to eliminate affected areas, improve ventilation and light conditions.
Fruits should not be harvested during wet conditions
General disease control strategies
Field sanitation
Graft to resistant rootstock
Pruning
Control vector that causes disease-apply IPM
Crop rotation
Use copper-based fungicides
Timely spraying
Proper site selection.
Maturity is determined by time after transplanting after bloom and external skin colour changes from green to yellow or purple, depending on the type of passion fruit
Seeded yellow passion fruit are mature 10 months after transplanting with full production occurring after 18 months
Grafted passion fruits begin initial production after 7 months.
Harvest is done manually by cutting or clipping the fruit off the vine using sharp knife or clippers with a sharp edge
Passion fruit for processing fruit drops to the ground when fully mature and they look shrivelled and unattractive, hence they are collected every second day
For fresh fruit and export markets fruits are picked after full colour development when the whole fruit is purple or canary yellow but before shrivelling and drying sets in.
Pack in 4.5 and 6 kg fibreboard cartons, sometimes in one or two layer trays or cell packs
Passion fruit subjected to free aerated place will shrink.
Harvested fruits should be handled with care and they should be placed in a plastic bucket or field container without dropping or throwing them
The harvesting container should also be clean to avoid any contamination.
Much higher yields are possible e.g. 50 tons per ha annually for purple passion fruit in Kenya.
Yields increase up to 3rd year. Beyond that the yields decline
Yields of over 6-8 tons per acre are attainable on Purple variety and 8-10 tonnes per acre of Esther purple variety.
Passion fruit is processed to make juice and jam

Juice

Jam
